Describe the Exchange of Gases in the Lungs
It is also referred to as external respiration as it involves the respiratory processes that have contact with the external environment. Pulmonary gas exchange takes place in the lungs between the alveoli and the blood.
Gas Exchange Physics Diffusion Barrier Teachmephysiology
While the bulk flow of air from the external environment happens due to pressure changes in the lungs the mechanisms of alveolar gas.

. This is driven by the change in partial pressure from the alveoli to the capillaries. External respiration is the formal term for gas exchange. The alveoli are small sacs surrounded by capillaries which are adapted for efficient gaseous exchange.
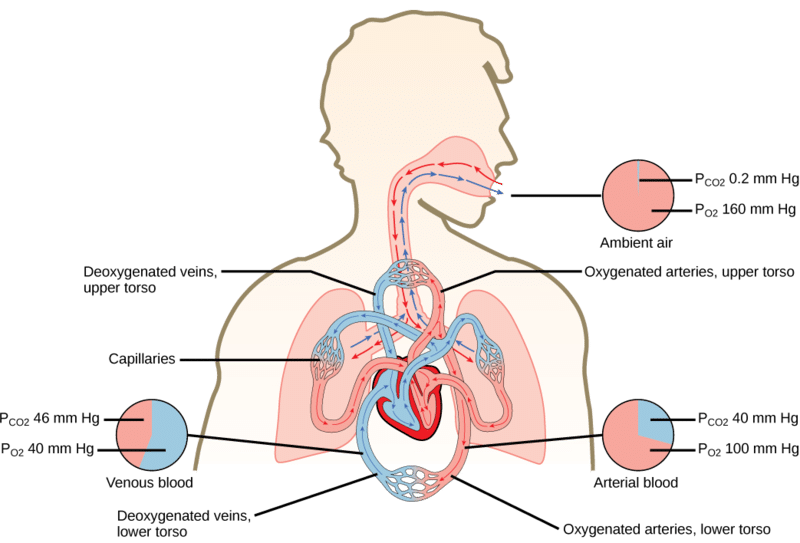
The function of the respiratory system is to move two gases. External respiration is the exchange of gases with the external environment and occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. In the lungs where oxygen is picked up and carbon dioxide is released at the respiratory membrane and at the tissues where oxygen is released and carbon dioxide is picked up.
Gas exchange is a process that involves the swapping of gases that occurs at exchange surfaces such as the alveoli found within your lungs. Inhaled oxygen enters the lungs and reaches the alveoli. Gas exchange occurs down a pressure gradient via a.
Tapeworm which infects the body and is a living organism is an example of what type of pathogen that causes illness. Describe the process of gas exchange between the lungs blood and tissues and the outline factors which influence this exchange. When we breathe out air the diaphragm relaxes which results in the decrease of chest cavity.
Structural and functional complexities of the mammalian lung evolved to meet a unique set of challenges namely the provision of efficient delivery of inspired air to all lung units within a confined thoracic space to build a large gas exchange surface associated with minimal barrier thickness and a microvascular network to accommodate the entire right ventricular cardiac. The primary function of the respiratory system is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Gas exchange in the lungs The cells in the body need oxygen to release energy from food efficiently by carrying out aerobic respiration.
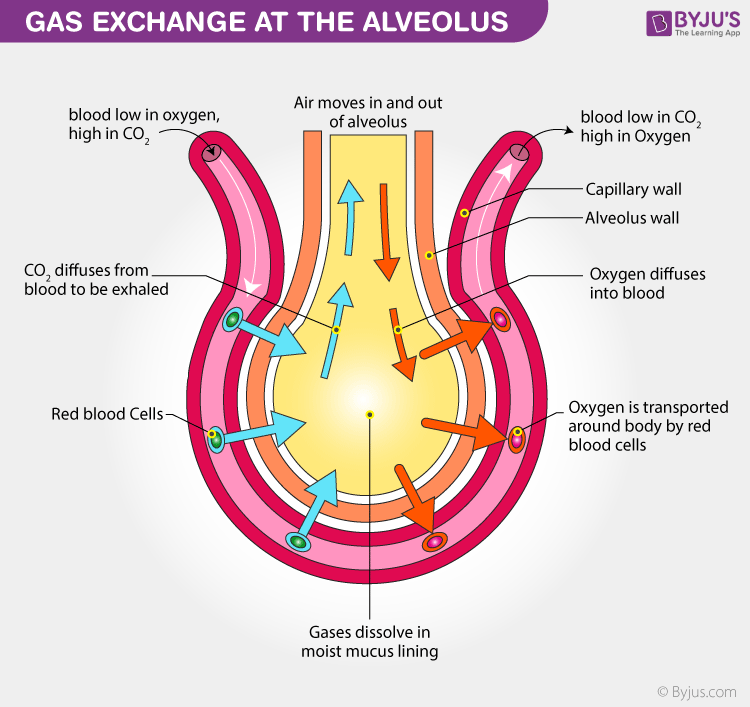
Now the air present in air sacs of the lungs is rich in CO 2. The layers of cells lining the alveoli and the surrounding capillaries are each only one cell thick and are in very close contact with each other. In very small organisms there is no need to have a separate transportation system for gases as all its cells are directly involved in the exchange of gases by diffusion.
The gas exchange that takes place in the lungs are carbon dioxide and oxygen. The exchange of gas occurs in the alveoli of the lungs. The lungs are the centerpiece of your respiratory system.
53 The solubility of oxygen in solution is relatively low necessitating the presence of hemoglobin to carry oxygen to active tissues. The exchange of gases between the blood capillaries and the tissues cells. Describe the nature of the movement of gases in the lungs including the factors that affect partial pressure of alveolar gases and tissues.
This diffusion is caused due to the differential partial pressure of the respiratory gases. PULMONARY GAS MOVEMENT AND EXCHANGE-In the conducting zone airways gas moves down a pressure gradient via bulk flow-In the respiratory zone gas diffuses across the respiratory membrane after dissolving in alveolar fluid-The. The exchange of gases between alveoli and blood takes place by the process of diffusion.
Gas exchange occurs in the alveoli where oxygen is exchanged with carbon dioxide between the alveoli and the blood in the capillaries. In the human body oxygen is used by cells of the bodys tissues to produce ATP while carbon. This contraction pushes the air from the lungs into the trachea nostrils and then out of the body into air.
The process of pulmonary gas exchange removes CO 2 from the blood and replenishes the bloods O 2 supply. Tapeworm which infects the body and is. Gas exchange takes place in the millions of alveoli in the lungs and the capillaries that envelop them.
When you inhale breathe in air enters your lungs and oxygen from that air moves to your blood. As shown below inhaled oxygen moves from the alveoli to the blood in the capillaries and carbon dioxide moves from the blood in the capillaries to the air in the alveoli. Details of breathing not required 4 Air travels thought the trachea bronchi bronchiole and reaches alveoli down a pressure gradient.
52 The exchange of gases occurs primarily within the lungs and tissues. Gases tend to move from a high-pressure area to a low-pressure one. Oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Gas exchange of CO2 for oxygen occurs between capillaries and ALVEOLI in the lungs. At the same time carbon dioxide a waste gas moves from your blood to the lungs and is exhaled breathed out. Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli to the blood in the capillaries and Carbon Dioxide diffuses from the capillaries to the alveoli.
Describe how oxygen in the air reaches capillaries surrounding alveoli in the lungs. Where does the exchange of gases occur inside the lungs. This process called gas exchange is essential to life.
The exchange of these gases occurs in the alveoli. Gas exchange of CO2 for oxygen occurs between capillaries and what structure in the lungs. The exchange of gases between the lung and the blood capillaries in the lung.
Gas exchange occurs at two sites in the body. It describes both the bulk flow of air into and out of the lungs and the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide into the bloodstream through diffusion.
Explore How Gas Exchange In The Lungs Takes Place In Vivid Detail

Every Breath You Take The Process Of Breathing Explained Nursing Times

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Describe the Exchange of Gases in the Lungs"
Posting Komentar